EMan Mold Intelligent Manufacturing Management System
Digitalized Full-process Management of Mold Manufacturing
The ongoing changes in market competition brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic, coupled with the continuous encouragement, support, and promotion of digital transformation by national and local governments, have led more and more enterprises to accelerate their digital transformation efforts in order to tackle increasing "uncertainties."
Although the importance of digital transformation is widely recognized across various industries, the path to transformation is often easier said than done for most manufacturing enterprises.
This difficulty arises from the significant differences among sub-sectors within the manufacturing industry and the unique characteristics of enterprises positioned at different points in the industrial chain. Consequently, the breakthrough points for digital transformation can vary greatly.
Taking the die and mould industry as an example, it is a sector characterized by production to order, unlike traditional mass production and planned manufacturing industries. Furthermore, it is marked by challenges such as difficulty in processing, long cycles, high precision, and stringent technical requirements. Therefore, the digitalization and automation initiatives of die and mould enterprises must fully consider these specific production characteristics.
So, how should die and mould enterprises invest in, advance, and evaluate their digitalization and automation transformation? Many companies likely share these questions.
This article addresses six key questions, providing a comprehensive analysis from top-level planning, method guidance, to technology empowerment. It interprets the two major standards released by the State Administration for Market Regulation, the Standardization Administration of China, the National Standard Information Platform, and the China Die & Mould Industry Association: the "Assessment Methods for the Digitization Capability of Die & Mould Enterprises" and the "Assessment Methods for the Automation Capability of Die & Mould Enterprises." The aim is to help mould enterprises overcome transformation obstacles, correctly understand intelligent manufacturing, and gain insights into the challenges and strategies for advancing their transformation.
Question 1
Q: What are the "Assessment Methods for the Digitization Capability of Die & Mould Enterprises" and the "Assessment Methods for the Automation Capability of Die & Mould Enterprises"?
A: They are the "stethoscopes" of the mould industry.
To effectively promote the digitalization and automation capabilities in die and mould enterprises, the China Die & Mould Industry Association proposed and organized the development of two group standards: the "Assessment Methods for the Digitization Capability of Die & Mould Enterprises" and the "Assessment Methods for the Automation Capability of Die & Mould Enterprises."

Cover Pages of the Two Standards
These standards provide a comprehensive map of digitalization and automation capabilities from three aspects: positioning, direction, and path. They help enterprises accurately determine their position, identify weaknesses in their digital and automated operations, recognize their strengths and weaknesses, and offer directional guidance for further digitalization and automation transformation. Based on assessment results, they provide enterprises with tailored, executable digitalization and automation transformation plans, assisting them in systematically and hierarchically achieving intelligent manufacturing goals.
As of October 1, 2021, these assessment methods were officially released and entered the implementation phase.Mould enterprises can voluntarily choose to conduct preliminary evaluations of either or both digitalization and automation capabilities based on their capacity enhancement needs.
Question 2
Q: Who are the developers of the two standards? Are they authoritative?
A: Initiated by the China Die & Mould Industry Association and jointly developed with over 10 leading domestic and international industry enterprises.
The two standards were initiated by the China Die & Mould Industry Association. They were primarily drafted by E-Mold Technology, which offers comprehensive digital production solutions for mould enterprises and enjoys 20 years of expertise, as well as Dongguan Mould, a global leader in injection moulding solutions. The drafting involved collaboration with 10 other industry players, including software system providers, machine tool manufacturers, mould companies, and academic experts such as Makino, Fanuc, Hexagon, FAW Mould, and the State Key Laboratory of Material Forming and Die & Mould Technology at Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
Initiating Organizations
Throughout the drafting process, the standards drew extensively on international concepts and practical experiences related to digitalization and intelligent manufacturing, while deeply considering the production characteristics and future development trends of the die and mould industry. These standards provide significant guidance for evaluating digitalization, automation capabilities, and related technologies within the mould sector, effectively assisting the industry in advancing its transformation towards intelligent manufacturing and enhancing manufacturing capabilities.
In summary, these two standards are the first authoritative and universally applicable professional assessment methods in the mould industry, filling the gap in evaluating digitalization and automation capabilities for this sector.
Question 3
Q: What capabilities are primarily assessed by the standards for digitalization and automation capability?
A: A comprehensive "health check" for the enterprise.

Scope of Digitalization Capability Assessment
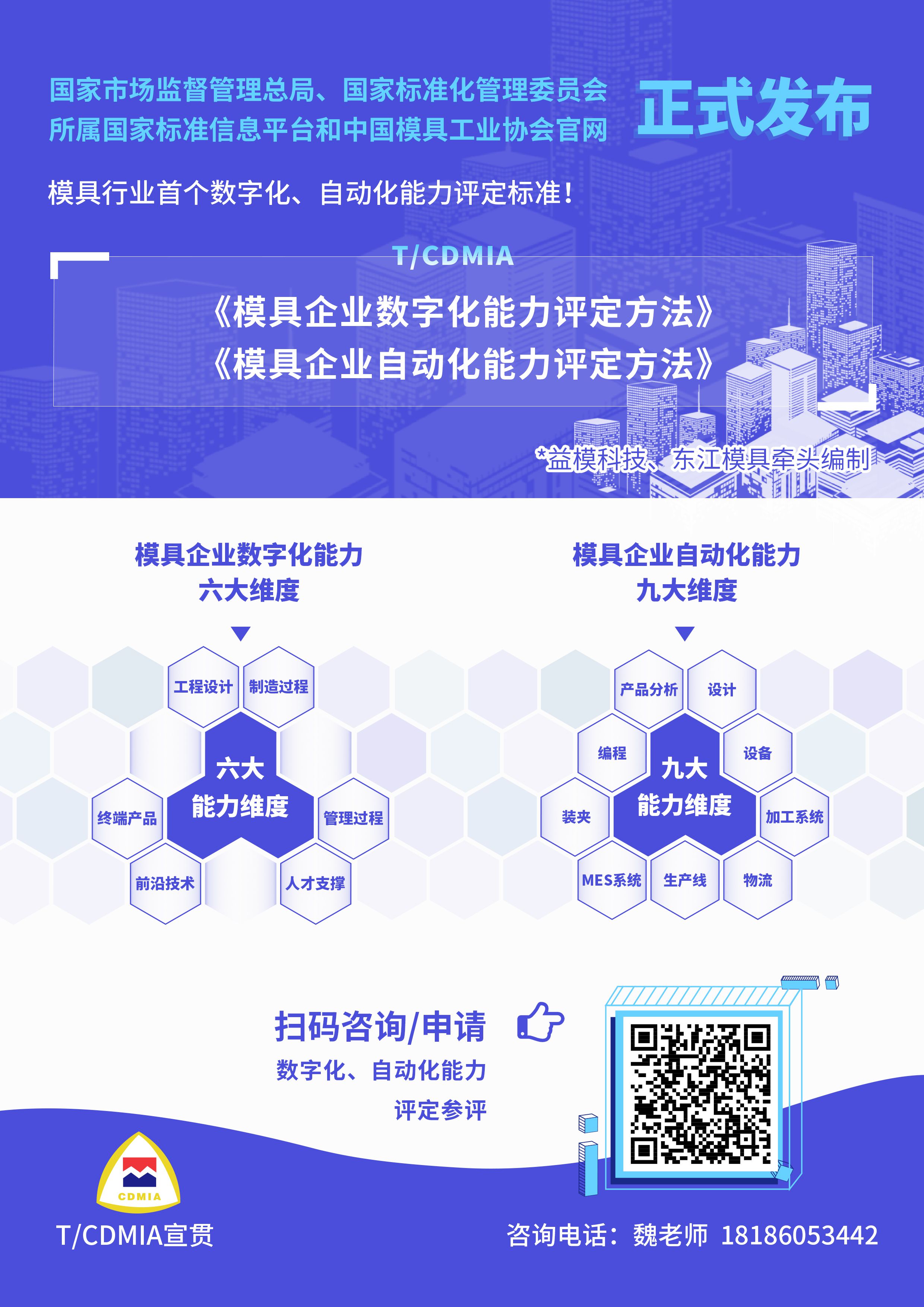
The digitalization capability assessment covers six major dimensions: engineering design, manufacturing process, end products, management process, frontier technologies, and talent support. It evaluates 19 sub-capabilities, including digital design, process, programming, production control, and more.

Scope of Automation Capability Assessment
The automation capability assessment is structured around nine dimensions: product analysis, design, programming, equipment, clamping, processing systems, MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems), production lines, and logistics.

Based on the capability assessment dimensions set by the two methods, enterprises can conduct self-assessments and scoring of various indicators according to their actual situations. The overall scores categorize enterprises into five assessment levels, from highest to lowest: Planning Level, Application Level, Standardization Level, Optimization Level, and Leading Level.
Question 4
Q: Why do die and mould enterprises need to participate in the assessment?
A: To assist in the high-quality transformation and upgrading of die and mould enterprises.
According to multiple industry survey reports, many companies have invested significant financial, human, and material resources but have not achieved the expected results.
Before the standards were released, the drafting team initially assessed several key Chinese mould enterprises as samples. The results showed that only 8% of enterprises were at the "Fifth Level (Leading Level)," 61% were at the "Fourth Level (Optimization Level)," and 31% were at the "Third Level (Standardization Level)."
These results indicate that most outstanding key mould enterprises are still in the optimization stage with room for improvement, highlighting the challenging journey of transformation and upgrading for Chinese industrial enterprises.
There are five primary reasons for the poor transformation outcomes: First, there is a disparity in understanding the concepts of digital transformation across different levels of the enterprise. Second, companies struggle to accurately assess the actual business value of digital transformation, making it difficult to set appropriate transformation goals. Third, the abundance of transformation options results in many ideas from various business and functional departments, but there is a lack of a clear path. Fourth, traditional work mechanisms within enterprises are not conducive to promoting cross-departmental and innovative changes like digitalization. Fifth, there is a lack of professional digital talent.
From strategy to execution, enterprises need to address a series of practical challenges. Solving these difficulties requires authoritative standards to help begin with top-level design, establish unified thinking, coordinate planning, and build mechanisms aligned with the enterprise's maturity in digitalization and automation. Only by doing so can enterprises continually strengthen their capabilities amid ongoing transformation and optimization, achieving greater returns on investment and maximizing the value of transformation.
Question 5
Q: How can enterprises participate in the assessment? What are the procedures?
A: Simple and straightforward.
Participating in the assessment is quite straightforward. Enterprises can complete the survey questionnaire provided in the appendix of the standard, tailored to their actual situation. Based on the responses, they then perform a self-assessment scoring. Finally, they use the scoring results to comprehensively evaluate their current capability level.
After self-evaluation, enterprises can apply for a capability level certification from the China Die & Mould Industry Association. This involves submitting an application form for capability level assessment. The association will then organize experts to conduct an on-site investigation and review at the enterprise. Following the evaluation, the expert panel will issue an assessment conclusion. Finally, the China Die & Mould Industry Association will announce the assessment results and award the certification to the applicant enterprises.
Question 6
Q: What are the benefits of the assessment for enterprises?
A: There are significant advantages.
Summary
A significant number of enterprises are diving into the wave of digitalization and automation transformation, which is beneficial for the entire mould industry as it progresses from manufacturing to "intelligent manufacturing." However, does the substantial investment truly yield results?
On one hand, enterprises may have doubts about how to verify the actual benefits brought by the transformation, identify the issues encountered during the process, and understand the gap between themselves and other leading companies. Many enterprises are still exploring and learning as they go.
On the other hand, there is an abundance of suppliers aiming to empower enterprise transformation, but the quality of their services varies greatly. The mould industry urgently needs official standards to guide and help companies conduct timely self-assessments, participate in evaluations, and understand their levels of digitalization and automation capability, allowing them to swiftly adjust their transformation paths. The release of the standards for assessing the digital and automation capabilities of mould enterprises not only provides a set of compliant and authoritative benchmarks for the industry but also directs mould enterprises towards a healthier and more efficient path in their digital and automation transformations.
Capability Map Explanation:
Function as a Ruler:Establish clear benchmarks for assessing the capability of an enterprise's digitalization and automation transformation. Use these two standards as the basis for gauging transformation and upgrading capabilities.
Serve as a Mirror: Utilize the standards to evaluate the current capability levels of enterprises, identifying skill gaps and deficiencies.
Act as a Ladder:Discover the right and suitable path for upgrading, helping enterprises recognize the areas and content that need improvement, thus paving the way towards excellence.
