EMan Mold Intelligent Manufacturing Management System
Digitalized Full-process Management of Mold Manufacturing
On October 29, the grand celebration of the 40-year journey of Chinese mold industries and the 40th anniversary of the founding of the China Mold Industry Association was held in Chengdu.
Director, Digitalization & Informatization Committee China Die & Mould Industry Association (CDMIA)and Chairman and General Manager of Wuhan EMAN Technology Co., Ltd., delivered a keynote speech titled 'The Digitalization Journey and Future Prospects of Chinese Mold Companies' at the event. He elaborated on three main aspects: the development course of digital technology in Chinese mold companies, the future outlook of digital technology development, and suggestions for digital transformation planning.

Mr. Yi led the guests at the event in revisiting the development journey of digital technology in China's mold industry. He covered the initial phase of technology introduction and challenging explorations, the intermediate period of independent research and continuous innovation, and the current new stage of intelligence and integration. He provided a detailed explanation of the key milestones and achievements in digital technology development over the past 40 years. Additionally, Mr. Yi offered forward-looking and practical strategic recommendations regarding the future development direction of Chinese mold companies, pointing the way for the industry's continued prosperity and digital transformation.

*The following are excerpts from the speech:
The Development History of Mold Digital Design Technology:
In the 1980s, with the advent of general CAD integrated software systems such as UG, Pro/E, and CATIA and professional CAE software like MOLDFLOW and AUTOFORM, mold digital design technology began to flourish.

In the 1990s, due to high costs and technical barriers, foreign CAD/CAE software was mainly used by large state-owned enterprises and foreign-funded enterprises, with a relatively limited range of applications. The design results only represented major parts, while other parts were not designed.
Since the 21st century, with the widespread application of foreign CAD/CAE software in China, secondary development has become prevalent. At the same time, domestic CAD software companies such as ZWSOFT and Huatian have launched their own mold design software. Additionally, Huazhong University of Science and Technology has independently developed a series of material forming CAE software, including injection molding (Huashu CAE), casting (Huazhu CAE), and stamping (Fastamp). Although domestic CAD/CAE has developed rapidly, the construction of its application ecosystem is still in the nurturing stage.
Development History of Digital Manufacturing Technology in Mold Industry:
In the 1980s, the mold industry began to introduce foreign CAM software and CNC equipment for mold processing and manufacturing, achieving a transformation from manual operations to simple mechanized production.

In the 1990s, large mold enterprises extensively applied CAM software, and some small and medium-sized enterprises also began to try its use. The application of CAM software gradually became universal in the mold industry.
Since the 21st century, with the urgent demand for cost reduction and efficiency improvement in the manufacturing industry, semi-automated intelligent processing has been gradually applied, and flexible automated production lines have been increasingly used in the mold industry, achieving automation in processes such as CNC/CMM/EDM; integrated application with CAD, CAE software has realized digitalization and informatization of the entire mold design, manufacturing, and inspection process.
Development History of Digital Management Technology in Mold Enterprises:
From the 1950s to the mid-1970s, China's mold manufacturing industry was still in the nascent and early development stages, with generally small production scales, typically operated by families or small workshops. Technical levels were relatively rudimentary during this period, with simple and crude production tools relying on personal experience and habits for production management.

In the 1980s, mold enterprises began to introduce CNC equipment, leading to an expansion in production scale, although they mainly consisted of small to medium-sized factories. The fitter contracting management model became the mainstream operational mode at that time, and some enterprises introduced ERP systems for cost calculation.
Since the 21st century, some mid-sized mold enterprises with a certain scale have emerged, and specialized and refined work division has become one of the mainstream management modes. Mold production management software vendors, represented by EMAN, emerged, realizing full-process information management from order receipt to delivery.
As the scale of enterprises continues to expand, some companies have entered a stage of centralized and coordinated management. This phase requires better resource integration, efficiency improvement, and cost reduction. Production scheduling has become a bottleneck issue for mold companies. The Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) system for molds has gained significant attention. Additionally, mold production management systems and ERP systems have begun to integrate data more deeply, achieving an application effect where the integration of heterogeneous systems results in an outcome greater than the sum of their parts (1+1>2).


FAW Mold's journey with digital technology reflects a broader trend within the domestic mold industry towards innovation and efficiency. Starting in 1997, the company moved from traditional manual drafting to using CAD software for 2D designs, initiating a shift towards paperless processes. After 2005, FAW Mold adopted 3D solid mold design and began exploring more advanced technologies such as associative design, knowledge engineering, and template design, which significantly improved the quality and efficiency of their mold design processes.
In terms of digital manufacturing technology for molds, FAW Mold stayed abreast of technological advancements by introducing CNC machining equipment in 2006. This shift from manual operations to mechanized processes enhanced both the efficiency and precision of their mold manufacturing. The collaboration with Wuhan EMAN in 2019 led to the creation of the first flexible digital automated production line for small mold parts in the country by 2022
In terms of digital management of molds, FAW Mold has progressively adopted digital strategies for process-based management, evolving from reliance on personal experience to standardized and information-driven production management. The implementation of a mold production management system in 2006, again in collaboration with Wuhan EMAN, enabled full-process digital management of mold manufacturing, boosting production efficiency and reducing costs.
TK Mold
TK Mold is a typical representative of Hong Kong-funded enterprises and a leading one-stop injection molding solution provider. The company primarily serves industries such as automotive, home appliances, packaging, medical, and personal care.

The digital technology application journey of TK Mold has closely followed, and even led, the industry applications of digital design, manufacturing, and management technologies in the mold sector: Since 1998, TK Mold has actively introduced specialized CAE/CAD software like Moldflow and UG for injection mold simulation analysis and design. In 2019, it adopted the EMAN modular design platform.
In terms of digital manufacturing technology for molds, TK Mold has kept pace with and even led the times. In 1989, TK Mold introduced MasterCAM programming software and its first CNC machining center. In 2002, it set up a precision department and introduced precision high-speed machining centers, beginning to take shape with the division of labor model. In 2011, it brought in a CNC five-axis machining center, exploring integrated process machining. Starting in 2014, TK Mold began exploring and gradually implementing flexible automatic composite lines (NC, EDM), precision CNC, and EDM flexible production lines, as well as the industry's first five-axis flexible steel production line. In 2020, it introduced the AGV logistics handling system.
Simultaneously, TK Mold's production management model has been continuously upgraded and refined. In 2005, TK Mold implemented an ERP system to achieve effective management of enterprise resources. In 2015, it introduced the EMAN mold production management system and integrated it with the ERP system to achieve unified data source management. It gradually incorporated advanced management systems like APS, SRM, and PDM/PLM, realizing full-process information management from order receipt to delivery. Today, TK Mold is deeply pursuing Industry 4.0, promoting the comprehensive digitization and informatization of mold processes, advancing towards becoming a lighthouse factory.
KAIHUA
Kaihua is a typical representative of private enterprises and is now a leading company in China's large-scale injection mold industry. It has four major business segments: automotive, medical, logistics, and home appliances, with an annual mold output of over 3,200 sets, serving more than 300 clients.

Kaihua has been continuously and actively exploring the application of digital technology. Since 2007, the company has been investing in digital technology applications, from mold management systems to CRM (Customer Relationship Management) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems, and further into technical standardization, production management, supply chain management, and automated production lines. Kaihua continually upgrades and refines its digital systems. The integration of various systems, such as the integration of ERP with production management systems, has enhanced data sharing and improved the coordination efficiency of business processes.
During the stage of rapid digital advancement, Kaihua has focused on promoting the construction of automated production lines, such as the graphite unmanned workshop and the flexible automated steel processing line, achieving automation and intelligence in its production process. Currently, Kaihua is exploring the development of an integrated digital molding workshop and building the factory of the future.
In his speech, Mr. Yi highlighted the significant role played by the China Die & Mould Industry Association in continuously promoting the digitalization and informatization development within the industry. Since hosting the first conference on the informatization of mold enterprises in 2008, the association has persistently organized various industry events. These efforts aim to provide companies with pathways for digital transformation, share cutting-edge technologies, and build platforms for exchange, thereby fully promoting the transition of enterprises into the digital and information age.

Mr. Yi also pointed out that currently, the extent of digital technology application varies across different enterprises. Medium to large enterprises, with their relatively abundant resources, have seen more extensive digital technology adoption. In contrast, smaller enterprises face challenges due to their relatively weak digital foundations. Additionally, the application of digital technologies across different sub-sectors and regions is also uneven.
In terms of the goals of digital transformation, companies generally aim to significantly shorten delivery cycles, improve production efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure product quality consistency, in order to gain an advantage in the fiercely competitive market. However, as they advance in digitization, companies also face challenges such as the rapid pace of technological updates and the shortage of digital talent. At the same time, policy support provides a valuable opportunity for companies' digital transformation.Regarding the future development prospects of enterprise digital technology, Mr. Yi proposed the following points:
Promoting the Comprehensive Development and Application of Domestic CAD/CAM/CAE Software
On the technological level of CAD/CAM/CAE software, domestic CAD software manufacturers have achieved independent innovation and rapid development. According to the latest analysis report, the market share of domestic 3D CAD software increased from 4% in 2022 to 6% in 2023. In the future, there is a need to further promote the deep integration and application of domestic mold CAD/CAE/CAM. Currently, domestic CAE research and development is mainly concentrated in universities. While core algorithms are comparable to foreign software, there is a lack of data accumulation and an effective development-application-feedback-optimization cycle. Policy guidance, capital investment, and collaboration across industry, academia, and research are needed to create excellent domestic CAE software and commercial enterprises.
Strengthening AI and Mold Industrial Software Application and Integration
In the application and integration of emerging technologies, the focus should be on strengthening the integration of AI technology with mold industrial software. Current AI applications include multimodal search engines that enable efficient searches of 2D, 3D, sketches, and images; AI-powered intelligent process compilation for one-click process matching; and AI vision technology for intelligent, seamless work progress reporting.
There should be a deeper application of digital and intelligent technologies, such as robotics and automated production lines, to help mold enterprises improve production efficiency, reduce costs, and achieve energy savings. Additionally, by building a platform for industry data sharing and enhancing innovation capabilities, these dispersed technologies can be integrated and shared. This integration allows many small and medium-sized mold enterprises to better integrate into the global industrial and innovation chains, with industry divisions focusing more on specialization and refinement.
When discussing recommendations for the digital transformation of mold enterprises, Mr. Yi addressed the current shifts in industry transfer and changes in factors:
From 2018 to 2022, there was significant demand growth in the Asian and Eastern European markets. Additionally, from a policy perspective, there is national guidance to encourage the orderly transfer of capital, technology, and labor-intensive industries from the eastern to the central and western regions, as well as from central cities to inland areas. There is also a strong push for industrial digitalization and the digitalization of industries, requiring effective tapping of potential in digital transformation, including job optimization and career transition.
Looking ahead, mold enterprises should plan to build all-encompassing, intelligent manufacturing factories with exceptional competitiveness. This involves comprehensive transformations in areas ranging from order processing to design, manufacturing, and logistics. The goal is to achieve integrated, holistic, and vertically integrated full-process digital and intelligent development.
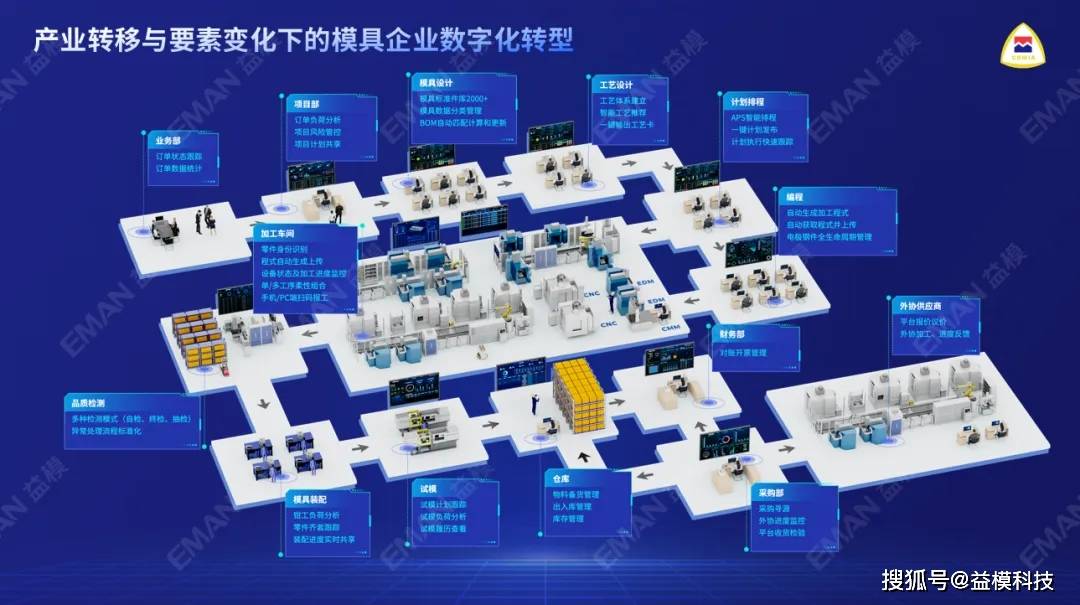
The four-stage roadmap for digital transformation in mold enterprises includes overall planning and phased construction:
Phase 1: Informatization Transparent Factory
Goal: Establish a production management system to achieve production transparency.
Main Content: This includes order management, project management, plan management, design management, process management, production execution, MDC collection, outsourcing management, visual dashboards, quality management, and programming/tool management.
Specific Measures: Build a digital transparent factory platform to enable traceability of the production progress and process of key components, implement paperless management in workshops, and ensure accurate real-time monitoring of equipment utilization rates.
Goal: Achieve localized automation based on a visual platform.
Main Content: Focus on automation to enhance efficiency in equipment programming processes, machining, logistics, and warehousing.
Specific Measures: Automate design, programming, and processing; automate machining and inspection; and automate warehousing and logistics. Also, emphasize efficient collaboration of people, machines, materials, and methods.
Phase 3: Lean High-Efficiency Factory
Goal: Achieve lean production operations using APS (Advanced Planning and Scheduling).
Main Content: This includes tool management, performance management, APS, supply chain collaboration, and lean production.
Specific Measures: Use lean production to arrange resources efficiently and respond quickly to enhance delivery capability, achieve coordinated manufacturing within the factory and across the supply chain, reduce manufacturing costs, and increase production profit.
Phase 4: Digital Intelligent Factory
Goal: Build a intelligence factory.
Main Content: Explore the application of process optimization, data mining, machine learning, digital twins, and AI with large models.
Specific Measures: Extract value from data at multiple levels and apply digital twin and AI technologies to achieve on-demand, highly flexible production, along with anomaly prediction and autonomous decision-making.
These four phases are executed progressively to realize digitalization, automation, lean processes, and intelligent manufacturing in the production process.
Automation Technology Application Roadmap for Mold Enterprises:

Prioritization of Parts Automation
Determine the priority order for the range of parts. Based on their own resource bottlenecks and actual processes, enterprises should focus on automating electrodes, inserts, mold cores, and other parts in sequence.
Standardization and Establishment of Norms:
Develop standards that include the normalization and standardization of data flow, zero-point positioning, design standardization, CAM standardization, and the standardization of clamping for electrodes and inserts.
Semi-Automated Processing and Part Identification:
During the semi-automated processing phase, complete RFID identification of parts. Through techniques such as CMM intelligent programming and EDM intelligent programming, various processing forms—including single-piece, batch, and flexible automated processing—are achieved with human intervention.
Unmanned Flexible Automation and Full Plant Automation:
Build flexible automated processing and complete plant automation, including process units, single-sequence track lines, and multi-sequence track lines. In terms of intelligent logistics, enterprises typically need to upgrade from manually operated stand-alone logistics to unmanned single-machine/multi-machine coordinated logistics, cross-production line coordinated logistics, and cross-workshop intelligent coordinated logistics, eventually achieving intelligent storage and logistics for the entire plant.
Beyond planning recommendations, Mr. Yi summarized the four common pitfalls and traps in enterprise digital transformation from aspects such as cognition, delivery, and operation & maintenance. He warned about the common challenges encountered during the digitalization process and provided industry assessment standards as method guidelines to help enterprises avoid pitfalls and successfully transition.
Key Points for Digital Transformation in Mold Enterprises:
Cognitive Introduction Phase:
Awareness Shift and Alignment with Organizational Culture
Executive Leadership:Establish the purpose of transformation and implement a "first-in-command" project, meaning the top executive (such as a CEO or director) personally leads, oversees, and ensures the implementation of the project.
Business and IT Departments: Align goals and clearly define internal business transformation needs.
Delivery Phase:
Clear Boundaries and Phased Implementation: Ensure collaboration and coordination throughout the process.
Operations and Maintenance Phase:
Scientific Selection and Long-term Experience Partnership:
Stable System Operation: Ensure the stable operation of systems.
Efficient Response Speed: Provide prompt and efficient responses.
Sustainable Maintenance Services: Offer ongoing maintenance services.
Extensible Business Data: Support the expansion of business data.
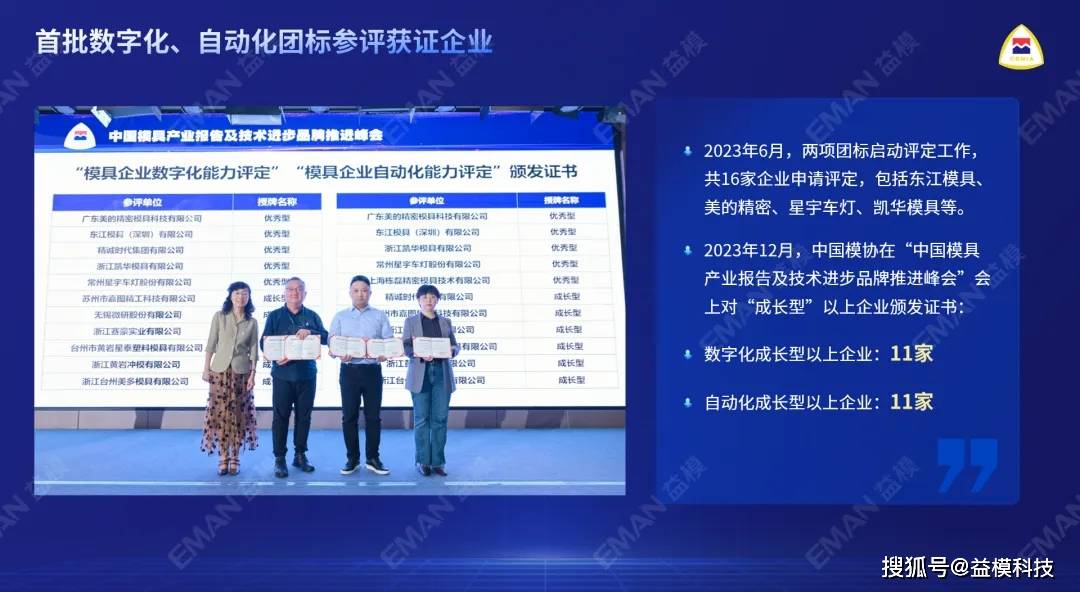
China Mold Association's Evaluation Standards for Digital and Automation Capabilities:
To effectively promote the development of digital and automation capabilities in mold enterprises, the China Die & Mould Industry Association has released two group standards: "Assessment Methods for the Digitization Capability of Die & Mould Enterprises " and "Assessment Methods for the Automation Capability of Die & Mould Enterprises."

Helping mold enterprises accurately position themselves involves identifying the digital and automation shortfalls in their production and operations, as well as recognizing their strengths and weaknesses. This provides direction for further digital and automation transformation, aiding enterprises in systematically and hierarchically achieving their smart manufacturing goals.
This document aims to offer a comprehensive and in-depth digital development report for Chinese mold enterprises, assisting them in better seizing historical opportunities and meeting future challenges to achieve sustainable and high-quality development. Additionally, it serves as a valuable reference and guide for researchers and practitioners in related industries and fields.

